Canadian Macromolecular Crystallography Facility - Insertion Device
The scientific goal of the CMCF-ID (08ID) beamline is to operate a protein crystallography beamline suitable for studying small crystals and crystals with large unit cells. Significant upgrades to the beamline were commissioned in May 2022, increasing the overall flux, enabling micro-focus beam sizes down to 5 µm, and significantly improving sample throughput.
The overall design of the beamline consists of white beam slits (WBS), an indirectly cryo-cooled double crystal multilayer monochromator (DCMM) supporting operation in monochromatic DCM mode or a high-flux "pink-beam" DMM mode, and vertical, horizontal, and micro-focusing mirrors. The innovative endstation utilizes an Arinax MD2-S microdiffractometer, Eiger X 9M X-ray detector, and ISARA sample automounter for rapid data collection both on-site and remotely. Beamline controls are based on EPICS and complemented with MxDC, a user-friendly interface developed in-house.
The source of X-rays on CMCF-ID is a small-gap undulator insertion device. As its name suggests, the undulator produces a periodic magnetic field that causes the path of the orbiting electrons to undulate, resulting in an emitted X-ray beam of higher spectral brilliance than could be produced by the simpler path taken by the electrons through a bending magnet.
The beamline is equipped with a Bruker XFlash 410 Spectrometer to perform X-ray Fluorescence spectroscopy and metal identification. The much higher flux of the CMCF-ID beamline makes it ideal for the collection of native datasets while still allowing for MAD/SAD data collection. Users are also encouraged to consider the use of CMCF-BM beamline for experimental phasing to reduce the risk of radiation damage.
Note: Data collection using the high-flux DMM mode poses a significant risk of sample destruction prior to full dataset collection, and is currently not recommended for most experiments. Users wishing to use DMM mode should reach out to your local contact well ahead of their planned beamtime.
Schematic
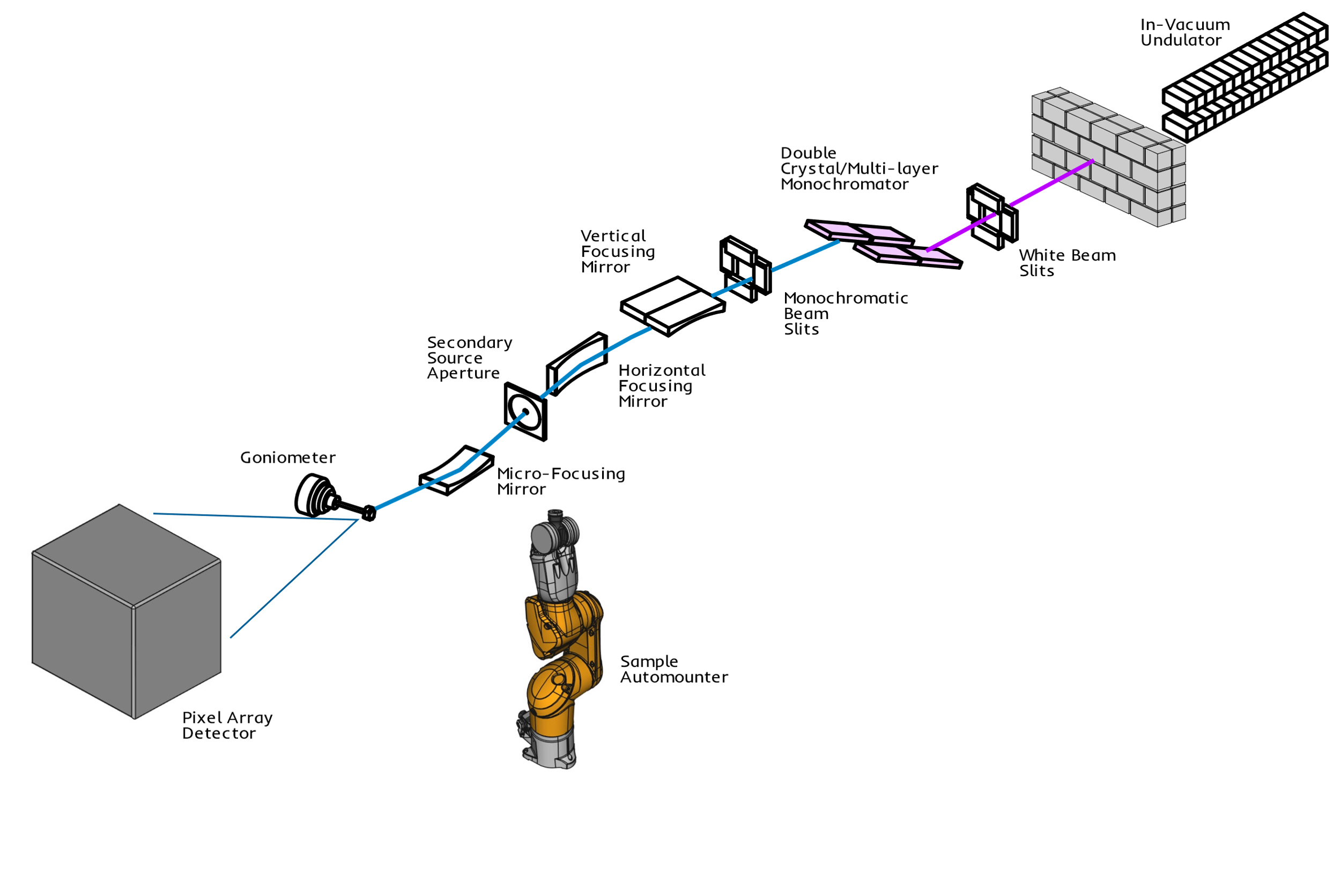
| Component | Distance from Source |
|---|---|
| WBS (White Beam Slits) | 40.3 m (Horizontal Slits) 41.5 m (Vertical Slits) |
| DCMM (Double Crystal Multilayer Monochromator) | 42.4 m |
| VFM (Vertically Focusing Mirror) | 46.5 m |
| HFM (Horizontally Focusing Mirror) | 48.4 m |
| μVFM (Vertically micro Focusing Mirror) | 50.4 M |
| Sample | 50.9 m |
Beamline Specifications
| Typical Ring Current | 220 mA (top-up mode) |
|---|---|
| Insertion Device | 20 mm asymmetric hybrid small-gap in-vacuum undulator (SGU) |
| Operational Gap Range | 5 mm - 15 mm |
|---|---|
| Number of Poles | 190 |
| Total Length of Magnet Assemblies | 3821 mm |
| Permanent Magnet Blocks | NdFeB Dysprosium |
| Minimum Remanance | 1.19T |
| Minimum Intrinsic Coercivity at 20°C | 39.0 kOe |
| Poles | Vanadium Permendur |
| Total Power | 11.4 kW (at 500 mA ring current) |
| Peak Flux Density | 1.066 T |
|---|---|
| Effective Flux Density | 0.981 T |
| Effective k | 1.83 |
| Higher Order Contributions | 8.4% |
| Photon Energy, n = 1 | 1.49 keV |
| Maximum Magnetic Load | 9.5 kN |
| Spectral Range (keV) |
DCM mode: 5.0-20.0 keV High flux DMM mode: 7.2-10.4 keV |
|---|---|
| Flux on Sample @ 200 mA (ph/s) |
DCM mode: 8.2 × 10¹² at 12 keV High flux DMM mode: 1.2 x 10 ¹⁴ at 9.72 keV |
| Flux density @ 200 mA (ph/s/mm²) |
DCM mode: 1.8 x 10¹⁶ DMM mode: 2.6 x 10¹⁷ |
| Energy Bandwidth (ΔE/E) |
DCM mode: 1.5 x 10⁻⁴ DMM mode: 1 x 10⁻² |
| Focal Size (FWHM) @ 12 keV (H x V) | 53.6 µm x 8.6 µm |
| Aperture sizes (µm) | 5, 10, 20, 30, 50 |
| Beam Divergence at Sample (H x V) @ 12 keV | 1.82 mrad x 0.34 mrad |
Beamline Hardware
| Monochromator | Axilon double crystal/multi-layer monochromator (DCMM) Comprising a pair of indirectly cryo-cooled SI₁₁₁ crystals (DCM mode) arranged in series with a pair of Mo/B4C-coated Si₁₁₁ multilayers (DMM mode) with 300 bilayers. |
|---|---|
| Mirrors |
Vertical Mirror: Si₀₀₁ with 2 stripes (Si, Rh/Ir). r.m.s. slope error 0.37 µrad Horizontal Mirror: Rh/Ir coated Si₀₀₁. r.m.s. slope error 0.78 µrad Vertical micro Focusing Mirror: Rh/Ir coated Si₀₀₁. r.m.s. slope error 0.15 µrad Mirrors form a Kirkpatrick-Baez configuration, with each mirror shaped using elliptical benders (FMB Oxford). |
| Horizontal Demagnification (1/Mx) | 6.8 |
| Vertical Demagnification (1/My) | 12.0 |
| Additional Instrumentation | Bruker XFlash 410 fluorescence detector, HC1 humidity control device |
|---|---|
| Pin Length | 18 mm Hampton Cryopin |
| Cryo Capability | Oxford Instruments Cryojet, 90-300K |
| Automounter | ISARA (single gripper) supporting Uni-Pucks, 464 pin capacity, approx 20 s duty-cycle |
| Goniometer | Arinax MD2-S microdiffractometer and SmartMagnet sample holder |
|---|---|
| Maximum Rotation Speed (deg/s) | 500 |
| Sphere of Confusion | 1 µm radius @ 100 deg/s |
| Type | Arinax B-Zoom On-Axis Visualization (OAV) |
|---|---|
| Orientation | Along beam axis |
| Zoom range | 2.5x-30x |
| Maximum Field of View | 2.4 x 1.9 mm |
| Minimum Field of View | 0.38 x 0.24 mm |
| Current Detector | Eiger X 9M |
|---|---|
| Output file format |
Datasets: HDF5 (.h5) Screening images: CBF (.cbf) |
| Crystal-Detector Distance | 120 mm - 1000 mm |
| Readout Time | Continuous readout, 3.0 µs dead time, duty cycle >99% |
| Max. rate | 238 Hz (16 bit). |
| X-ray Sensitive Surface (W x H) | 245.2 x 233.2 mm (57,180.64 mm²) Si-diode array, 450 µm thickness |
| Head Dimensions (W x H x D) | 34.0 x 37.0 x 50.0 cm |
| 2Θ Range | 20° - not currently in use |
| Resolution | 3,110 x 3,269, 75 x 75 µm pixel size |
| Detector History |
May 2017 - May 2020: Pilatus3 S 6M April 2010 - February 2017: Rayonix MX300 CCD Before April 2010: Rayonix MX225 CCD |