Research Highlights
GETTING TB OFF STEROIDS
For over 40 years, tuberculosis has been treated using a cocktail of antibiotics that must be taken for six months to a year. A discovery by researchers from the CLS and the University of British Columbia sheds light both on the source of the TB bug’s resilience and a new way to treat the infection
Aug. 24, 2010
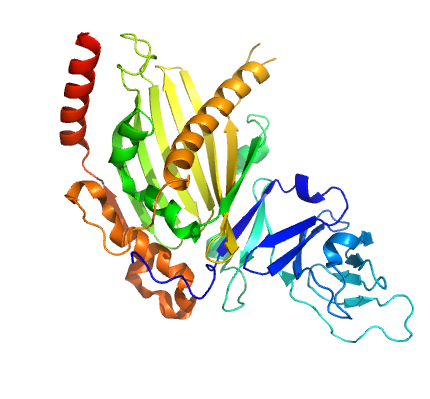
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the bacteria that causes tuberculosis, is a resilient organism that can only be effectively treated by a lengthy course of multiple drugs. Mtb is able to survive by harvesting the cholesterol stored in white blood cells. Researchers from the University of British Columbia used the 08ID-1 beamline to collect data about the strucuture of KshAB, one of the enzymes used to break down cholesterol. This structural information can be used to design drugs to interfere with the enzyme and develop improved drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis.
Acta Crystallogr. F 64 (9), 805-808