Research Highlights
INVESTIGATING THE MINIMAL PARP STRUCTURE
Understanding ADP-ribosylation is important to cell regulation often overlooked despite its role in some forms of inflammation and cancer.
April 1, 2024
A number of post-translational modifications (PTMs) exist to control the function and metabolism of biomolecules within the cell. ADP-ribosylation is a less understood PTM which has been linked to the regulation of the cell cycle and response to nutritional stress. Disruption of ADP-ribosylation proteins (PARPs) are indicated in multiple forms of inflammation and cancer.
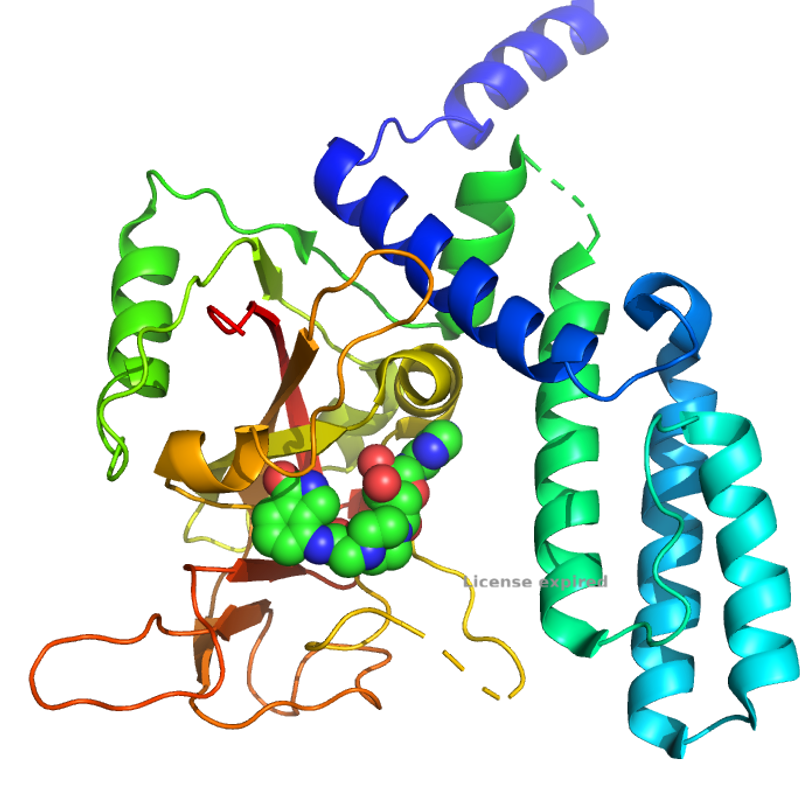
Researchers from the Pascal group have solved the structure of the novel PARP4 protein, a unique multidomain protein with an unknown function. The structures of apo-PARP4 showed a catalytically active "open" conformation only previously observed in homologues when RNA is bound. The effect of non-catalytic domain mutations suggest a role of RNA binding on moderating the protein activity without domain remodelling, presenting new questions into the interactions between these domains in various PARP homologues.